
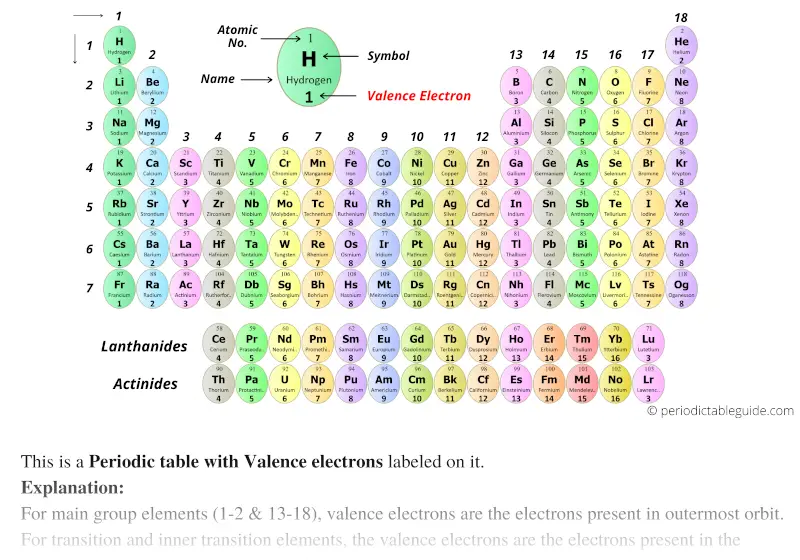
- Periodic table of elements with valence electrons full#
- Periodic table of elements with valence electrons series#
| 5th period: Mo, Ag, Cd, Sn | 6th period Pt, Au, Hg, Bi.
Periodic table of elements with valence electrons full#
In the full periodic table, Groups 3 to 12 contain the transition elements including: Periods and groups for the first 20 elements: group (vertical), period (horizontal). The relative atomic mass of Carbon, C, is defined as Metallic properties are dominant towards the lower left corner and non-metallic properties are dominant towards the upper right corner. It is the average of the values for the different isotopes of the element. The relative atomic mass is shown below the symbol for each element. It is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. The atomic number is shown above the symbol for each element. The groups have group notation numbers, 1 to 18, as approved by the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). The periodic table shows each element as a symbol with its atomic number atomic mass (whole number) electron notation and valence. The periodic table is an orderly way to arrange the properties of the elements. The periodic table organizes elements and it can be used to make predictions about the properties of elements.

They are colourless, odourless, monatomic gases and they form very few compounds.ġ.10.1 Introduction to the periodic table Group 18 elements are the noble gases (inert gases or rare gases) He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn-222. IUPAC has approved these new heavy elements, 114 Fl (Flerovium) and 116 Lv (Livermorium) (1 June 2012). Group 17 elements are the halogens, F, Cl, Br, I, At. The newest element is Copernicum, Cn, atomic number 112, discovered in 1996, but not given its symbol, Cn, by IUPAC until 2010. Groups are shown as vertical columns numbered 1 to 18, see top row. (This is not true if you group the transition elements together in the table.)
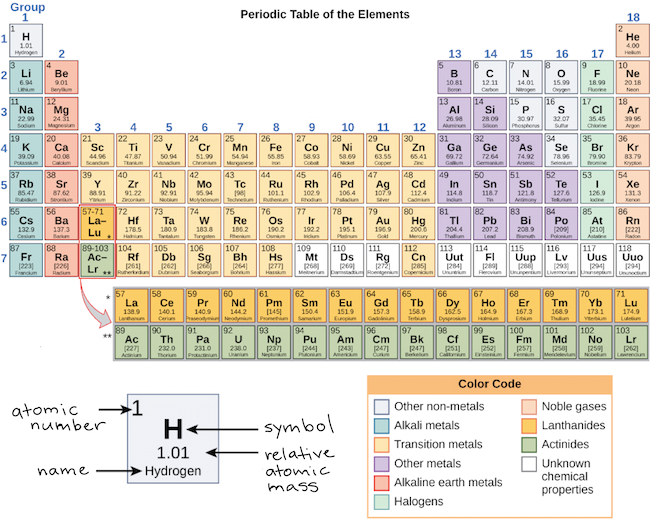
Some periodic tables using 1a, 2a to 0, suggest there are 18 groups.Įlements in the same group in the periodic table have similar chemical roperties, because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shells. Groups are the arrangement of elements in the periodic table. List of highest to lowest electronegativity Hydrogen is less electronegative than polonium and more electronegative than nitrogen, so the formulae of water is H 2O and the formula of ammonia is NH 3. Ignoring lanthanides and actinides, for two elements in different groups, the element in the higher numbered group has higher electronegativity,įor two elements within the same group, the element with the lower the atomic number has the higher electronegativity. Precious metals are those usually used in jewellery including Gold, Iridium, Palladium, Platinum, and Silver.Įlectronegativity is based on the IUPAC electronegativity listĮlectronegativity is the degree to which an atom attracts electrons.
Periodic table of elements with valence electrons series#
of the second and third transition series of the Periodic Table. Noble metals are commonly only Gold and Silver, but also can refer to metallic chemical elements resistant to oxidation or corrosion, including: Ruthenium, Rhodium, Palladium, Silver, Rhenium, Osmium, Iridium, Platinum, and Gold, i.e. Nordic Gold, a gold-coloured alloy, often used in coins, is made of 89% copper, 5% aluminium, 5% zinc, and 1% tin. In the common or industrial classification of metals, the following descriptions of metals are not chemically exact terms:īase metals are neither noble nor precious, are not resistant to oxidation, are common and are readily available with many uses, including Aluminium, Copper, Lead, Nickel, Tin and Zinc.Ĭoinage metals are copper, gold and silver, but this description of metals is not a chemically exact term. Mg 2+.ġ.3.0 Common or industrial classification of metals They easily lose two electrons to form ions, e.g. They are harder and have higher melting points and boiling points than the alkali metals. Group 2 elements are the alkaline earth metals, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra. Hydrogen is considered separately, because it has few of the properties of the alkali metals. They all have one valence electron that they lose easily to form ions. They react easily with water, have low melting points and densities, and are good conductors of electricity. The alkali metals are all soft, shiny and metallic when cut. Group 1 elements include the alkali metals, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr. Transuranic elements have atomic number > 92Īlkali metals: Lithium, Li, Sodium, Na, Potassium, K, Rubidium, Rb, Caesium, Cs, Francium, Fr Introduction to the periodic table: 1.10.1 See: Periodic table, An official website of the United States governmentĬommon or industrial classification of metals: 1.3.0


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
